
However, NIPT can already be accessed through numerous private clinics and hospitals across the UK for around £500. NIPT for these conditions has recently become available to pregnant women in the higher chance category in the NHS in Wales, and it has been promised to women in England and Scotland in the near future. You still get some false positive results, but far fewer than with older screening tests.
NIPT has been shown in multiple studies to be very good at identifying the most common chromosomal conditions – Down’s syndrome, Edwards’ syndrome and Patau’s syndrome – particularly in women who have a higher chance of having a fetus with one of these conditions. This is a newish kind of screening test in which a blood sample from a pregnant woman is used to test for a range of genetic conditions in the fetus, with varying levels of certainty.

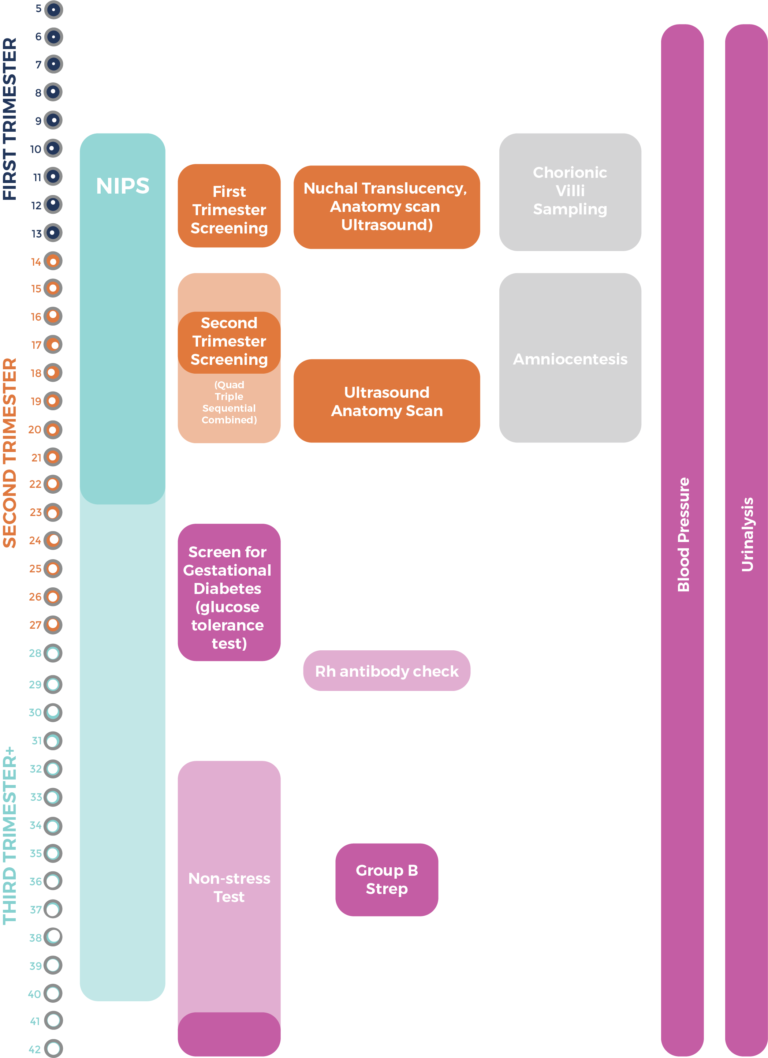
With NT, Nasal Bone, DV and first trimester serum (hCG and PAPP-A), FTS has a detection rate of 96-97%. The obstacle in providing FTS is largely due to limited resources for ultrasound training. Globally, 90 countries perform FTS as part of nationalized programs. Screening programs in Ontario and Alberta utilize FTS. If FTS performs so well, why isn’t it covered by MSP in BC?įTS is widely offered. For this reason, combined IPS is not popular. However, it is very hard not to disclose the results of the ultrasound to a patient without a lot of patient anxiety. In this form, IPS performs very similar to FTS in detection rates. In its pure form, IPS is sometimes performed as a ‘combined’ test, meaning that the first and second trimester blood and ultrasound results are not disclosed to the patient until completion of the second trimester blood work. This means that 12% of affected pregnancies are missed by this screen. This type of sequential testing performs at a 88% detection rate and is inferior to FTS (NT, nasal bone, ductus venosus Doppler, and FTS blood work). In BC, IPS is performed as a sequential test: this means that the NT is performed at 12 weeks, and if the NT is large, the patient is offered amniocentesis or CVS, or they can wait for the rest of the blood work later in the pregnancy.

IPS involves adding a Nuchal Translucency (the 12 week ultrasound test to measure the pocket of fluid at the back of the fetal neck) in addition to SIPS blood work. Note that the PAPP-A measurement is not disclosed to the patient or the doctor, until the quadruple screen is completed. This means that 16-18% of affected pregnancies are missed by this test. It performs at a 82-84% detection rate for 5% false positives, and is an improvement on the quadruple screen. SIPS involves taking blood in the first trimester (12 weeks) for PAPP-A analysis, and then adding in a quadruple screen in the second trimester (16-20 weeks) giving a final result after the quadruple screen. Serum Integrated Prenatal Screening (SIPS) It gives a detection rate of 72-75%, with 5% false positives, and this means that 25-28% of affected pregnancies are missed by this test. Is a blood test at 16-20 weeks which looks for four different proteins.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
